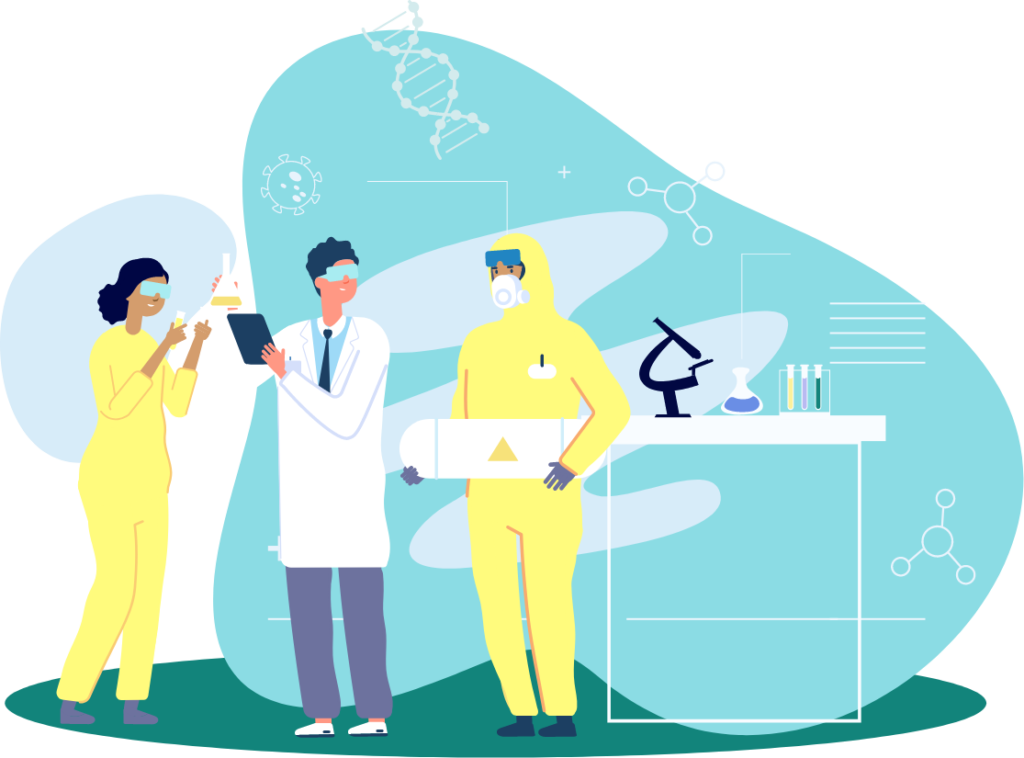
Vaccines are complex biological products with lengthy manufacturing and control processes. The change from discovering a vaccine
for a disease to manufacturing gallons of safe vaccines for mass production is dramatic. 5
After the infection, the immune system remembers what it learned about how to protect the body against that disease and can respond rapidly to destroy the germ the next time the body is exposed.


Vaccines contain parts of or weakened versions (inactivated or attenuated)
of a particular germ. Vaccination exposes the body to parts of the germ for the first time without causing disease, and subsequently, the real germ can be rapidly destroyed
if it enters the body to prevent illness. 9
Vaccine Supply & Demand:
HIDDEN MASTERY AND UNSEEN EFFORT...


When we turn on a tap, we expect clean water to come rushing out on demand. However, we’re often not aware of the amount of work and effort that has gone into bringing the water to our homes.
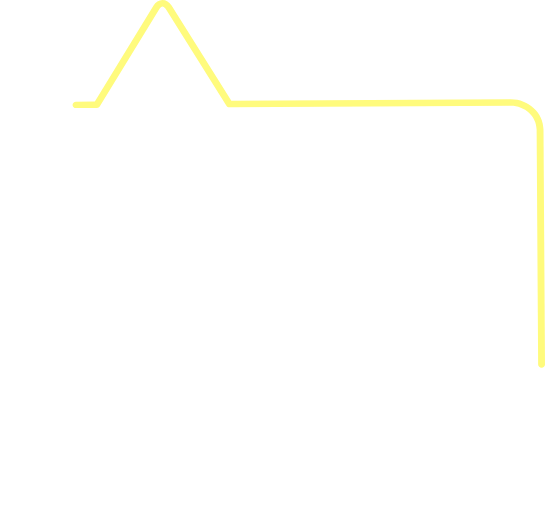
The same can be said for vaccines – there is an incredible amount of time, care and effort which goes into the development of each and every vaccine.
The work involved in creating a vaccine
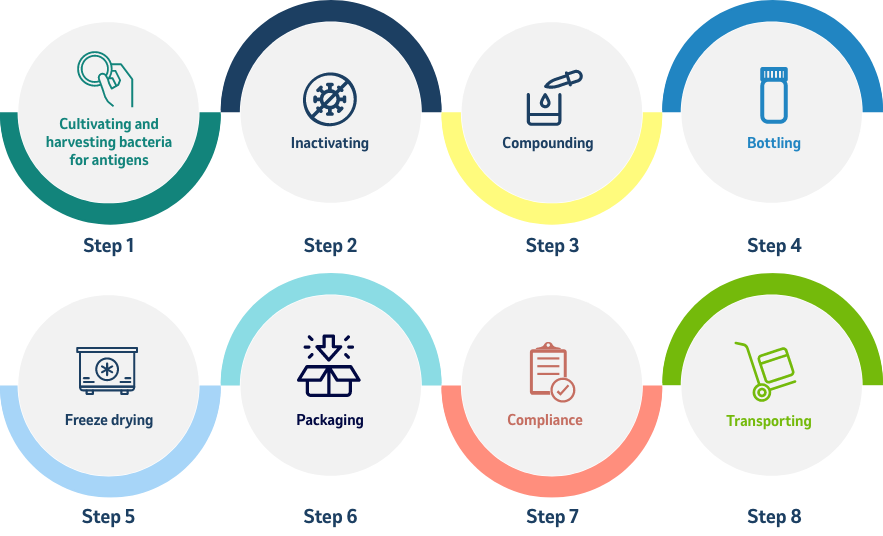
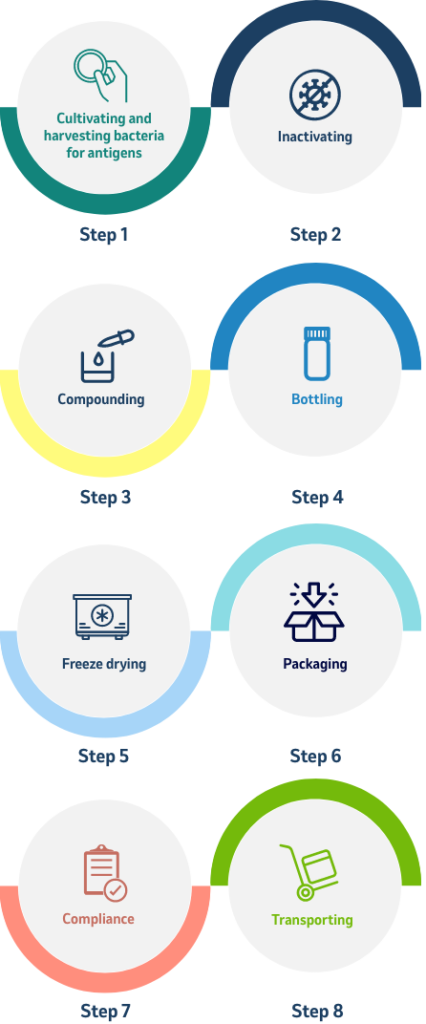
Quality Control is Essential
Precision in quality control is essential: To protect both the purity of the vaccine and the safety of the workers who make and package the vaccine, conditions of laboratory cleanliness are observed throughout the procedure.
All of these operations are conducted under sterile conditions, and all instruments used are sterilized in an autoclave (a machine that kills organisms by heat, and which may be as small as a jewel box or as large as an elevator) before and after use. 10

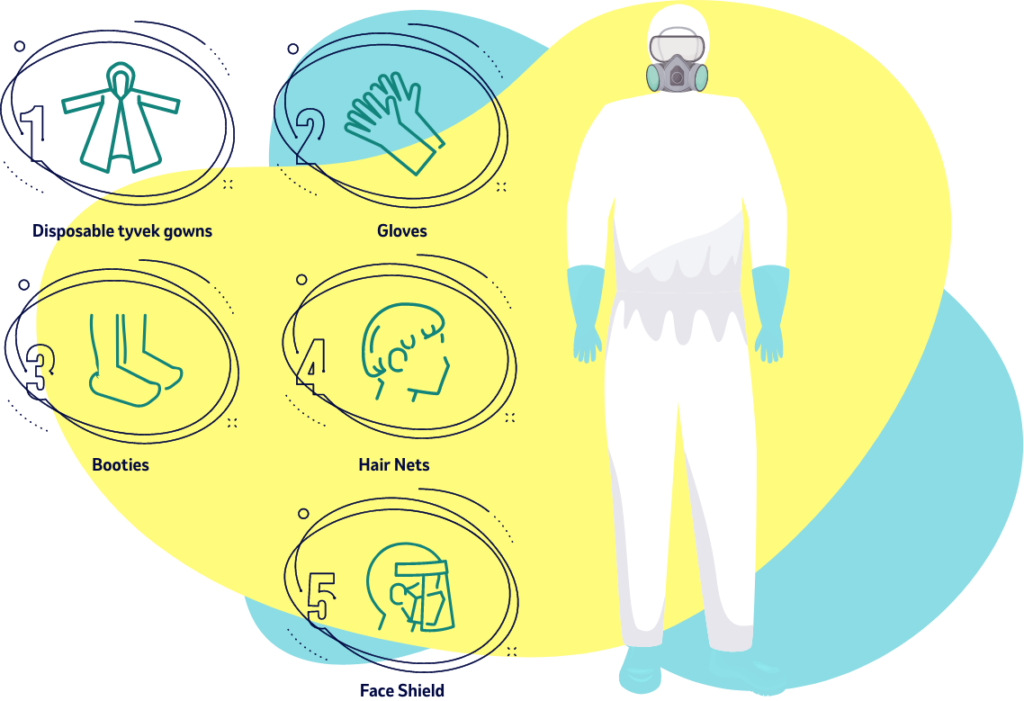

Protection Is Key

Manufacturers such as MSD are required to ensure that products under their control are maintained under appropriate conditions so that the identity, strength, quality, and purity of the products are not affected. 8

Acquiring regulatory approval:
Production processes are continually adapted in order to meet evolving regulatory demand which varies country-by-country.
This is why precision and an intense focus on safety and quality is critical to the development of every vaccine, to ensure that the finished product meets necessary regulatory standards. 5

MSD continues to increase
our production capacity to respond
to the rising demand for vaccines
throughout the world.
To learn more about how MSD is responding to the COVID-19 pandemic, click here
New or expanded immunisation programmes around the world have created an unprecedented increase in global demand for vaccines, including many produced by MSD.
In addition, the production process is under even greater pressure as demand for certain vaccines grows, and as demand increases from the global public health community to investigate new and emerging threats.